
SECTION 4.5ABSOLUTE VALUE ANDRECIPROCALS OF POLYNOMIALFUNCTIONS
© Copyright all rights reserved to Homework depot: www.BCMath.ca

I) REVIEW
Line Equation:
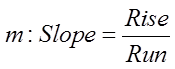
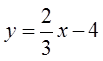
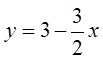

II) ABSOLUTE VALUE FUNCTION
The absolute value of any real number willbecome positive
Negative Positive
Positive Positive
Note: An absolute value function will take anypoint with a negative y-coordinate and change itto a positive y-coordinate
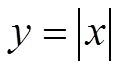
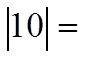
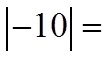

III) GRAPHS OF ABSOLUTE VALUE FUNCTIONS
The ABS function will reflect any part of the functionunder the x-axis to above the x-axis
The ABS of a straight line is a V-shape
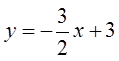

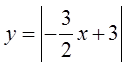
The center of the graph is atthe x-intercept
There are two sides: Left & Right

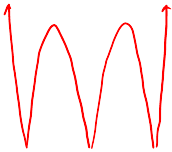
ABSOLUTE VALUE OF CUBIC FUNCTIONS
Suppose you’re given the graph of the polynomial
Parts of the graph under the x-axis will be reflected up
x
y
-3
-2
-1
0
1
2
-4
-2
2
4
6
x
y
-5
-4
-3
-2
-1
0
1
2
3
4
5
-10
-8
-6
-4
-2
2
4
6
8
10

IV) SOLVING ABSOLUTE VALUE EQUATIONS
When solving abs equations, the value inside the abssign can be both positive or negative
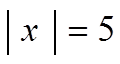
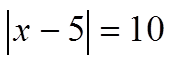
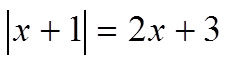
So when we are solving abs functions, we need toconsider both cases
After we solve for “x” in both cases, plug it back into theequation to check for extraneous roots
Extraneous roots will occur when the y-value isnegative

x
y
-10
-8
-6
-4
-2
0
2
4
6
-2
2
4
6
The solutions are: x= -8 & x= 2
Now check for extraneous roots byplugging “x” back into the originalequation
If we are to solve this equationgraphically:

PRACTICE: SOLVE
No Solutions
There is only onesolution at x = 0
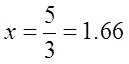
There is only onesolution at x = 1.666…
Extraneous Root

PRACTICE: SOLVE
x
y
-3
-2
-1
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
-2
2
4
6
x
y
-3
-2
-1
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
-2
2
4
6
Only one intersection at x=0
Only one intersection at x=1.66
Extraneous
Root

V) SOLVING ABSOLUTE VALUE INEQUALITIES
Solve for all intersections points
Number Line Test Points
Check which Domain satisfies the inequality
Solve for Intersections points
Make a number Line
Create Test Points
Only one region satisfythe inequality

PRACTICE: SOLVE THE INEQUALITIES
Extraneous Root
b/c right side willbe negative
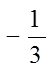
Soln.
Soln.
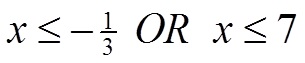

CHALLENGE:
Both sides of the numberline yield no solutions. Sothe only point that satisfies theinequality is at x = –2
No Solution!
There are no intersection pointsSo we only need one test point
Extraneous
Solution: X can be all real numbers