
SECTION 8.2NETS OF 3D OBJECTS
© Copyright all rights reserved to Homework depot: www.BCMath.ca

I) REVIEW: RECTANGULAR PRISMS
Prisms are 3D objects where two opposite sides areparallel and have the same shape
A rectangular Prism is a prism where the opposite endsare rectangles/squares
© Copyright all rights reserved to Homework depot: www.BCMath.ca
Triangular Prism
Pentagonal Prism
Hexagonal Prism


PYRAMIDS AND OTHER SOLIDS:
A pyramid is a solid where you have a flat base and allthe side merge onto a point
Rectangular Pyramid
Hexagonal Pyramid
Triangular Pyramid
Cylinder
Cone
Sphere
© Copyright all rights reserved to Homework depot: www.BCMath.ca
Discuss:What are the differencesbetween Prisms andPyramids?

SURFACE AREAS
The surface area of a 3D object is the sum of areas of allthe faces
For instance, when looking at a cube, there are six sides
Each side is a square
When we are finding the surface area, calculate thearea of all six sides and take the sum
Front
Back
Top
Bottom
Left
Right
Total SA =
© Copyright all rights reserved to Homework depot: www.BCMath.ca

PRACTICE: FOR EACH OF THE FOLLOWING SOLIDS, INDICATETHE NUMBER OF SIDES AND WHAT SHAPE IT IS.
Triangular Prism
Pentagonal Prism
Front
Back
Left
Right
Bottom
Front
Back
Bottom
Left
Right
There are 5 sides to this 3D solid
There are 7 sides to this 3D solid
© Copyright all rights reserved to Homework depot: www.BCMath.ca


WHAT ARE NETS?
A net is an enclosure of an object that is laid flat
Used for finding the surface area of a 3D solid
For instance, play the video to see how a net for a cube iscreated:
© Copyright all rights reserved to Homework depot: www.BCMath.ca

Practice: Given each of the following nets, indicate whatthe solid it is:
TriangularPrism
Cylinder
PentagonalPyramid
Cone
TriangularPyramid
Nothing
Nothing
Rectangular
Pyramid
© Copyright all rights reserved to Homework depot: www.BCMath.ca


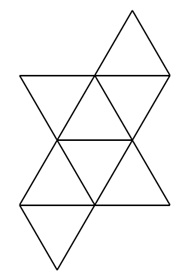
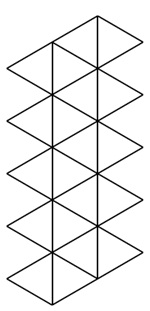
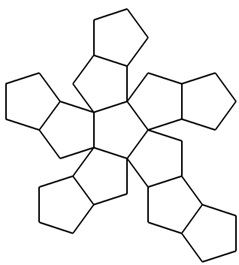
CHALLENGE: CAN YOU SEE WHAT 3D SOLID ISMADE FROM THE FOLLOWING NETS?
© Copyright all rights reserved to Homework depot: www.BCMath.ca

CHALLENGE: SUPPOSE A FLY IS SITTING AT ONE CORNEROF A BOX. WHAT IS THE SHORTEST DISTANCE THAT THEFLY NEEDS TO TRAVEL TO GET TO THE OPPOSITE CORNER?
The fly can’t travel through thebox but only on the surface
What is the length of the shortestdistance travelled?
The shortest distance is32.01 cm
