
SECTION 7.6PROBABILITY WITHCOMBINATION & PERMUTATIONS
© Copyright all rights reserved to Homework depot: www.BCMath.ca

REVIEW: PERMUTATIONS & COMBINATIONS
Permutations refers to the numbers of ways a group of objects canbe arranged, such that the order is important
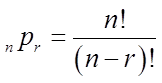
Combinations refers to the numbers of ways a group of objectscan be arranged, such that the order is NOT important
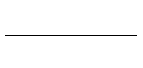
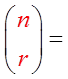
“r” is the number of objects chosen &
“n – r” is the number of objects NOT chosen
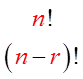
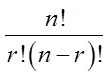
© Copyright all rights reserved to Homework depot: www.BCMath.ca

Ex: with a deck of 52 cards, how many 5 card hands are possible?
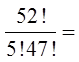
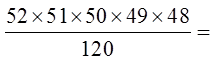
Ex: A “flush” contains all 5 cards with the same suit. How manyflush hands are there?
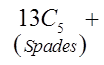
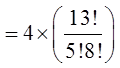
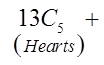
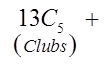
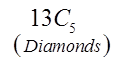
Ex: How many hands with atleast 3 spades?
Need to consider the hands with 3, 4, and 5 spades
© Copyright all rights reserved to Homework depot: www.BCMath.ca

Ex: 5 people are in a race: Amy, Ben, Chris, Don, and Ed. Howmany different outcomes are possible?
Ex: If only 1st, 2nd, and 3rd places are taken, how many possibleoutcomes are there?
Ex: Given the letters: SWOOOSSHH, how many permutationsare possible?
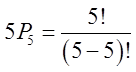
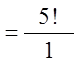
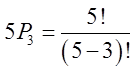
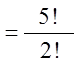
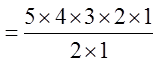
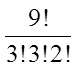
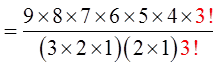
© Copyright all rights reserved to Homework depot: www.BCMath.ca

PROBABILITY WITH PERMUTATIONS & COMBINATIONS:
When solving probability with counting principles involved:
first find the total number of desired outcomes and
Divide it by the total number of possible outcomes
Ex: What is the probability of being dealt the following five cardhands?
a) Flush with spades
b) Full house with 3 kings and 2 aces
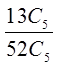
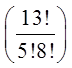
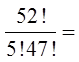
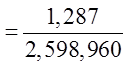
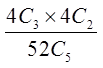
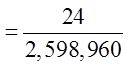
© Copyright all rights reserved to Homework depot: www.BCMath.ca

Ex: Four cards is drawn from a deck, what is the probability ofnot getting any diamonds?
b) What is the probability of getting atleast one diamond?
Use the complement to find this probability:
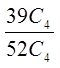
Choose 4 cards from a deck of 52
39 cards that are not diamonds
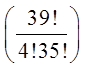
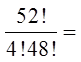
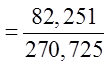
© Copyright all rights reserved to Homework depot: www.BCMath.ca

Practice: What is the probability of getting a five card hand with3 hearts and 2 spades?
b) What is the probability of getting a seven card hand with 4 redcards and 3 spades?
c) What is the probability of getting 4 spades, 2 hearts, and 1 clubfrom a 7 card hand?
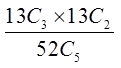
Use the bucket method to find the total number of desired hands
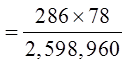
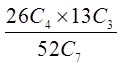
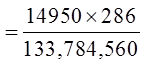
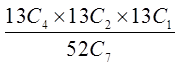
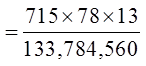
© Copyright all rights reserved to Homework depot: www.BCMath.ca

EX: THERE ARE 12 HORSES IN A RACE WITH 1ST, 2ND, AND 3RDPLACES. WHAT IS THE PROBABILITY THAT SOMEONE WILL GETALL THREE HORSES IN THE CORRECT ORDER?
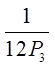
Order matters, so its a permutation
Only 1 correct outcome
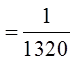
PRACTICE: IF THE ORDER OF THE HORSES IS NOT TAKEN INTOACCOUNT, WHAT IS THE PROBABILITY THAT SOMEONE WILLCORRECTLY GET ALL THREE HORSES?
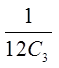
Order doesn’t matters,so its a combination
Only 1 correct outcome
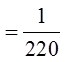
© Copyright all rights reserved to Homework depot: www.BCMath.ca

IN THE LOTTO 649 DRAW, 6 NUMBERS ARE DRAWN FROM 1TO 49 WITHOUT REPLACEMENT. WHAT IS THE PROBABILITYOF EACH EVENT?
a) Four out of six numbers are correct
b) Five out of six numbers are correct
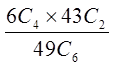
Order doesn’t matters,so its a combination
43 other numbers that you didn’tchoose, 2 of them were in the lottery
Out of the 6 numbers you chose,4 of them are correct
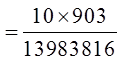
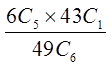
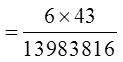
© Copyright all rights reserved to Homework depot: www.BCMath.ca

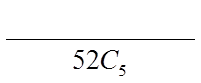
Ex: When given a five card hand, what is the probability ofgetting a full house ( 3 of a kind and a pair)
Note: there are 13 different values to choose for the pair and 3 of a kind
Out of the 13 values, there are 13 choices for the triple
For each value, there are 4 suits: (Spade, hearts, diamonds and clubs)
For the three of a kinds, out of the 4 suits, choose 3
For the pair, out of the 4 suits, choose 3
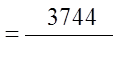
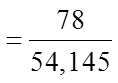
© Copyright all rights reserved to Homework depot: www.BCMath.ca
Then there are 12 values left for the pair

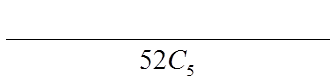
Challenge: When dealt a five card hand, what is theprobability of getting 2 pairs?
Note: there are 13 different values to choose for each pair and the single card
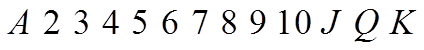
The first pair and second pair can be intertwined 13 choose 2
For each pair, there are four suits, and you choose two out of the four
For the single card, you have 4 cards and choose 1
© Copyright all rights reserved to Homework depot: www.BCMath.ca
For the single card, there are 11 options left, so multiply by 11
Note: the difference between the fullhouse (permutation) and thetwo pairs(combination) is that the pairs can be in any order

HOMEWORK:
Pg. # 3, 5ab, 6-11, 13-16, 18, 20
© Copyright all rights reserved to Homework depot: www.BCMath.ca

PROBABILITY OF GETTING 2 PAIRS
Out of the 13 choices, choose 2 for the pair
Draw a bucket to separate each group
Out of the deck of 52 cards, 44 cards are left for thesingle card because it can not be the same as eitherone of the pairs
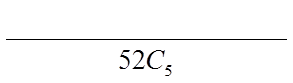
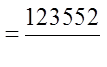
© Copyright all rights reserved to Homework depot: www.BCMath.ca