
SECT 5.3 TRIGONOMETRICIDENTITIES PART 1
© Copyright all rights reserved to Homework depot: www.BCMath.ca

WHAT IS A TRIGONOMETRIC IDENTITY?
A trigonometric identity is an equation that is equal for allvalues of the variable(s) for which the equation is defined
Examples of trigonometric identities
Trigonometric equations that are not Identities
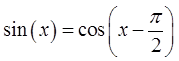
© Copyright all rights reserved to Homework depot: www.BCMath.ca
Equation is true only at certain values of “x”
Both sides are equal for all values of “x”
Graphically, if both sides overlap each othercompletely, then the equation is an identity
Graphically, both sides only intersect at certainpoints, then the equation is NOT an identity

ODD VS EVEN IDENTITIES:
Even Identities: An function that looks the same when reflectedover the y-axis (Horizontal Reflection)
Odd Identities: A function that looks the same when reflectedover both the X and Y axis
























x
y
-1
1
























x
y
-1
1
© Copyright all rights reserved to Homework depot: www.BCMath.ca

PYTHAGOREAN IDENTITIES:
Review: The coordinates of any point on the circumferenceof an unit circle can be represented by:
X-coordinate
Y-coordinate
Since:
PythagoreanIdentity
Other Pythagorean Identities can be generated by dividing allterms by either “cos2x” or “sin2x”
© Copyright all rights reserved to Homework depot: www.BCMath.ca

BASIC IDENTITIES
Odd- Even Identities
Reciprocal Identities
Quotient Identities
Pythagorean Identities
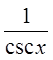
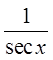
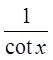
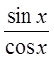
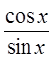
© Copyright all rights reserved to Homework depot: www.BCMath.ca
Other identities can be created by manipulating the equation

VERIFYING AND PROVING IDENTITIES
There are two ways to Verify an identity
Plug variety of numbers into the equation
If the equation is equal for all the values, then theequation is an identity OR
Graph the equations, if they completely overlap, then it’san identity
Proving an Identity
Simplify the equation algebraically and then show thatboth sides are equal
When proving algebraically, first convert all functionsinto sine or cosine
Then simplify using basic identities
© Copyright all rights reserved to Homework depot: www.BCMath.ca

EX: VERIFY THE FOLLOWING IDENTITY:
NUMERICALLY:
GRAPHICALLY:
Pick a random number
Both sides are equal!
Pick another number
Both sides are equal again!
























x
y
-4
-3
-2
-1
0
1
2
3
4
-2
-1
1
2
Since the graphsoverlap each other
completely, then it
must be an identity
© Copyright all rights reserved to Homework depot: www.BCMath.ca
Since the equation is equal for bothverifications, then it’s likely to be anidentity

PRACTICE: VERIFY THE FOLLOWING IDENTITIES NUMERICALLY:
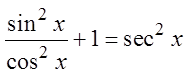
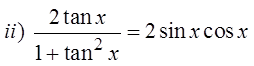
© Copyright all rights reserved to Homework depot: www.BCMath.ca
Pick a random number for “x”
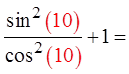
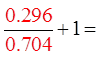
Try another value for “x”
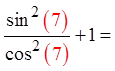
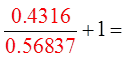
Both sidesare equal
Since the equation is equal forboth verifications, then it is likely to be an identity
Make “x” = 10 rad.
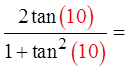
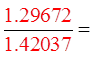
Make “x” = 2 rad.
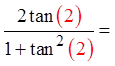
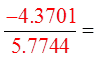
Both sidesare equal
The equation is likely to
be an identity

PRACTICE: VERIFY EACH OF THE FOLLOWING IDENTITIES:
Numerically:
Graphically:
© Copyright all rights reserved to Homework depot: www.BCMath.ca
























x
y
-2
-1
1
2
Numerically:
Graphically:
Not an Identity!!
























x
y
-2
-1
1
2
